Top Ingredients to Look for in Anti‑Aging Skincare Products
Share
Introduction
Aging is a natural process, but the way skin responds over time can be influenced by what we put on it. The right skincare ingredients don’t promise immortality, but they can significantly reduce visible signs of aging—fine lines, loss of firmness, dull tone—and support the skin’s barrier so it stays resilient. For those seeking to support skin’s radiance and structural integrity, understanding which ingredients are both effective and safe is essential. Here, we’ll explore key anti‑aging ingredients, how they work, what to avoid, and how to incorporate them into your routine smartly—so your skin can look its healthiest and most radiant self.
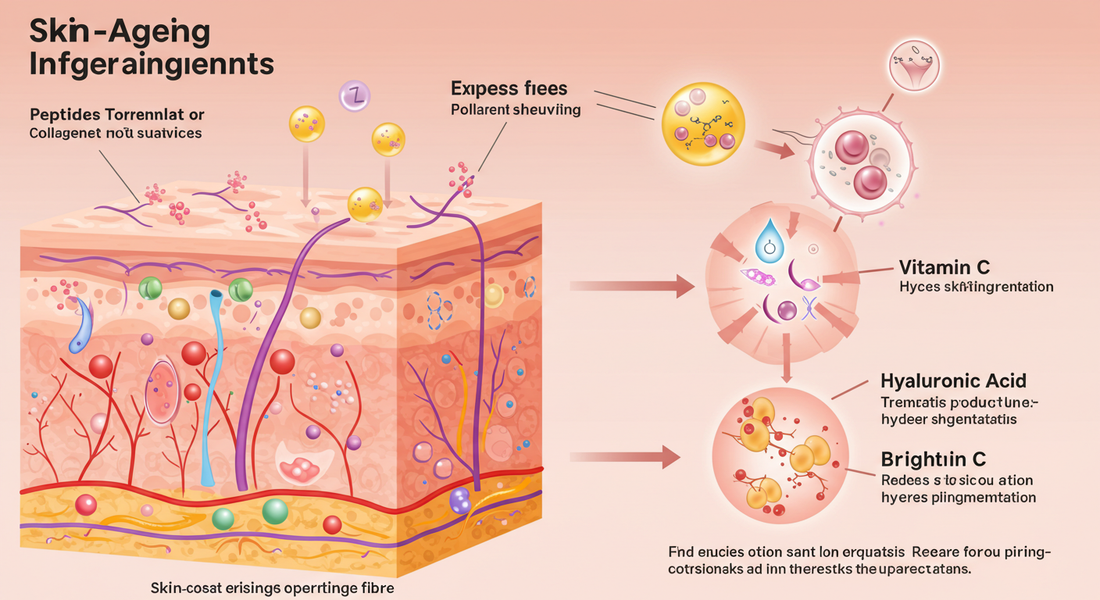
1. Retinoids / Retinol
Retinoids are derivatives of vitamin A and are among the most studied and proven ingredients in anti‑aging skincare. They work by stimulating cell turnover, boosting collagen production, and fading pigmentation. Regular use can help reduce fine lines, improve skin texture, and even skin tone.
Because retinoids can be irritating—especially for sensitive skin—start with lower strengths. Use a pea‑sized amount in your night routine. Leave gaps of a few nights in between uses at first, then gradually increase as your skin tolerates it. Always pair retinoids with a moisturizer to prevent dryness or peeling.
2. Peptides
Peptides are short chains of amino acids that act as signals to the skin, telling it to produce more collagen and repair matrix structures. They are gentler than strong actives like retinoids, making them suitable for daily or near‑daily use, often in serums or lightweight creams.
Some peptides also help reduce inflammation, support elasticity, and improve firmness. They can be especially useful in combination with other anti‑aging actives to cushion or support the skin when more aggressive ingredients are present.
3. Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
Hyaluronic acid is a powerful humectant—an ingredient that draws water into the skin and retains it. Because water is crucial for skin’s plumpness and elasticity, HA can make the skin appear smoother, softer, and less wrinkled almost immediately.
Different molecular weights of hyaluronic acid penetrate at different skin depths. A formula with a mix of high and low molecular weight HA often gives both surface hydration and deeper moisture, helping reduce the look of fine lines while maintaining skin comfort.
4. Antioxidants (Vitamin C, E, Ferulic Acid, etc.)
Antioxidants protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals—unstable molecules generated by UV exposure, pollution, and smoke. Without protection, free radicals accelerate aging, dark spot formation, and loss of elasticity.
Vitamin C is a heavyweight antioxidant: it brightens pigmentation, evens skin tone, and can support collagen synthesis. Pairing vitamin C with vitamin E and ferulic acid enhances stability and efficacy. Antioxidants are best used during the day under sunscreen for maximal protection.
5. Niacinamide
Also known as vitamin B3, niacinamide is versatile, well tolerated, and has a broad range of benefits. It helps strengthen the skin’s barrier, reduce redness, regulate sebum production, fade spots, and improve texture. For aging skin, niacinamide’s barrier support and gentle brightening are especially valuable.
Niacinamide works well in serums or moisturizers. It can be combined with retinoids and antioxidants to amplify benefits while minimizing irritation.
6. Ceramides and Lipid‑Restoring Ingredients
With age, the lipid barrier of skin may weaken, reducing its ability to retain moisture and protect against environmental aggressors. Ceramides are lipids naturally present in skin, and using ceramide‑rich products helps restore that barrier integrity.
Other lipid‑restoring ingredients include cholesterol, fatty acids, squalane. These ingredients help reduce transepidermal water loss, soothe sensitive or reactive skin, and improve overall texture and resilience.
7. Exfoliants (AHA, BHA, PHAs)
Exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells, improving texture and radiance, and allows other actives to penetrate more effectively. For anti‑aging, chemical exfoliants are preferred to physical scrubs, because they are less likely to cause microtears.
Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid and lactic acid help smooth surface roughness; beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), like salicylic acid, penetrate pores and help reduce congestion; polyhydroxy acids (PHAs) are gentler and often better for sensitive or compromised skin.
Use exfoliants 1‑3 times per week depending on skin tolerance and strength of the acid. Over‑exfoliation can lead to irritation, inflammation, or increased sensitivity to sun.
8. Sunscreen / UV Filters
Even when you choose the best anti‑aging ingredients, if skin is unprotected from UV exposure, many of their benefits are undone. UV radiation is perhaps the most significant external factor accelerating skin aging: causing collagen breakdown, pigmentation, thinning of skin, and loss of elasticity.
Broad‑spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher is non‑negotiable. Physical filters like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are often gentler, especially for sensitive skin. Reapply sunscreen every two hours when in direct sunlight.
9. Ingredients to Avoid or Use with Caution
While focusing on potent ingredients, it is equally important to know what might harm or counteract skin progress if misused.
Strong essential oils, high concentrations of fragrance, alcohol denat. in high amounts can disrupt barrier, especially in mature or sensitive skin. Harsh physical exfoliants or abrasive scrubs risk microtears. Very strong retinoids should be introduced slowly.
10. How to Incorporate These Ingredients into Your Routine
Constructing an effective routine with anti‑aging ingredients needs strategy and patience. Here is a general way to add and layer these ingredients safely:
- Start with a basic routine: gentle cleanser, moisturizer, sunscreen in the morning; gentle cleanser, moisturizer at night.
- Introduce one new ingredient at a time—perhaps an antioxidant in the morning, then a retinoid at night. Use each new product for several weeks before adding another.
- Use gentle, hydrating moisturizers alongside potent ingredients to support barrier health.
- Reserve exfoliants for non‑active nights if using strong actives (e.g. avoid exfoliants on nights when using retinoids).
- Monitor skin reactions—redness, peeling, excessive dryness—and adjust frequency or strength accordingly.
Common Mistakes & Best Practices
Avoiding mistakes is important to prevent setbacks. Some frequent missteps include using multiple strong actives at once, skipping sunscreen, overlooking how seasonal changes affect skin, or expecting immediate dramatic results. Best practices revolve around consistency, gentleness, and gradual progression.
Conclusion
The most powerful anti‑aging skincare is built on proven ingredients, careful usage, and respect for skin’s natural rhythms. Retinoids, peptides, antioxidants, ceramides, niacinamide, and gentle exfoliants all play specific roles; it’s the way they are used in combination that makes a difference. At Lune Skin, formulating products that blend efficacy with gentleness is core to our mission. When these ingredients are incorporated thoughtfully, skin can retain its radiance, strength, and texture through every phase of life.
